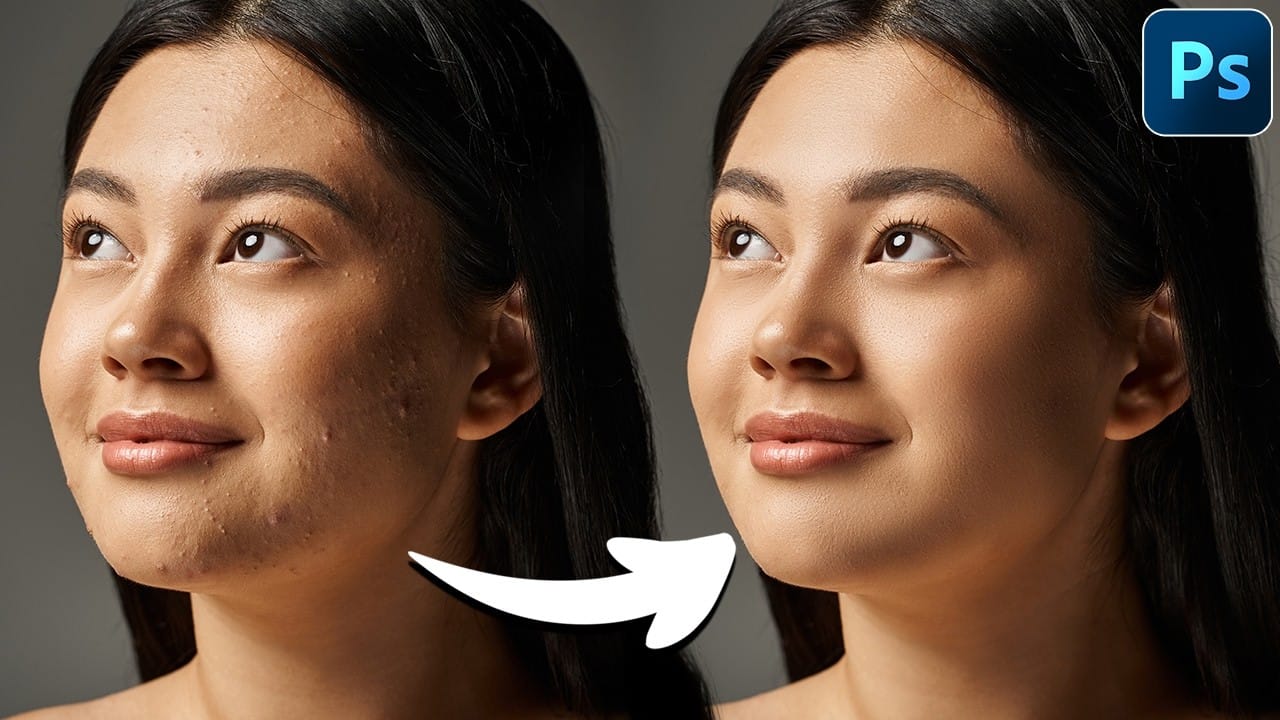
In photography, achieving flawless subject skin can often be a challenge. Blemishes, uneven tones, and harsh shadows frequently detract from an otherwise great photo, leading to frustration for both photographers and subjects.
This guide explores frequency separation, a powerful technique that allows precise skin retouching without sacrificing natural texture. Learn how to apply this method, enhance it with advanced steps, and integrate tools that streamline your workflow for professional results.
Watch the video
Any links or downloads mentioned by the creator are available only on YouTube
Breaking It Down
Frequency separation is a Photoshop technique that separates the image into two distinct layers: one containing color and tone information (low frequency), and another holding fine details and textures (high frequency). This separation enables you to smooth skin while preserving crucial details like pores and skin texture, avoiding an artificial, plastic look.
Before applying frequency separation, it is crucial to perform blemish removal. This non-destructive step uses tools like the Remove Tool, often accessed by pressing J.
Ensure you work on a new layer, with Sample All Layers enabled and Remove After Each Brush Stroke disabled in the options bar, allowing for efficient, single-pass cleanup.
The core of frequency separation involves creating specialized layers. Begin by duplicating your merged base layer twice, naming the top layer texture and the bottom blur. Apply a Gaussian Blur (Filter > Blur > Gaussian Blur) to the blur layer, setting the radius until textures are just out of view.
For the texture layer, use Image > Apply Image, select Subtract as the blending mode, target the blur layer, and set Scale to 2 and Offset to 128. Finally, change the texture layer's blending mode to Linear Light to reveal the separated texture.
Practical Tips
- Perform all blemish removal on a dedicated, non-destructive layer before initiating the frequency separation process to prevent unwanted artifacts.
- Utilize the
Lasso Toolwith a feather radius (e.g.,10 pixels) on theblurlayer to isolate and selectively smooth areas of uneven tone, ensuring natural transitions. - To expedite iterative smoothing, create a custom keyboard shortcut for
Gaussian BlurviaEdit > Keyboard Shortcuts, allowing quick reapplication of the filter within selections. - After applying Gaussian blur, refine skin tones and shadows using the
Mixer Brush Tool. Set all blend settings (Wet, Load, Mix, Flow) to20%for subtle, buildable blending, particularly effective for blending hot spots or blotchiness. - Exercise caution when applying blur near hard edges like hairlines or clothing, as over-blurring can lead to undesirable color bleeding or an unnatural appearance.
Related Tutorials
Explore further resources and enhance your Photoshop skills with more in-depth tutorials and helpful downloads.